Flash Loan Attacks 101: Learn About Types of Flash Loan Attacks, Their Execution, and Prevention Measures.
BUILDBEAR // TUTORIALS
Flash Loan Attacks 101: Learn About Types of Flash Loan Attacks, Their Execution, and Prevention Measures.
What Is a Flash Loan?
A flash loan is a unique type of uncollateralized, short-term loan available in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space. Unlike traditional loans that require collateral, flash loans enable users to borrow cryptocurrency without providing upfront collateral. These loans are executed through smart contracts and are accessible for a very short duration, typically within a single transaction block.
If you are new to flash loans: Learn how to execute Flashloan here
How Do Flash Loan Attacks Work?
Flash loan attacks exploit the unique features of flash loans to manipulate markets, exploit vulnerabilities in DeFi smart contracts, or carry out fund theft from protocols. These attacks typically involve the following steps:
- Borrowing: The attacker initiates a flash loan from a DeFi platform, borrowing a significant amount of cryptocurrency without providing any collateral upfront. The loan is obtained and settled within the same transaction block.
- Execution: With the borrowed funds in their possession, the attacker can manipulate the price of a specific cryptocurrency by executing large buy or sell orders on decentralized exchanges (DEXs). This manipulation can create artificial price movements that favor the attacker's position.
- Repaying: To ensure the success of the attack and maintain the integrity of the flash loan, the attacker repays the borrowed funds within the same transaction block. By promptly repaying the loan, the attacker eliminates the need for collateral and minimizes the risk exposure for themselves.
The key element that makes flash loan attacks successful is the ability to execute all the necessary steps within a single transaction block. This time constraint and the absence of collateral requirements make it challenging for lending platforms to mitigate the risks associated with such attacks effectively.
Types of Flash Loan Attacks
Flash loan attacks can manifest in various forms, depending on the specific vulnerabilities or manipulation tactics employed by the attackers. Here are a few common types:
1. Price Manipulation: Attackers can exploit flash loans to manipulate the price of a targeted cryptocurrency. By executing large-volume trades within a short time frame, they can artificially inflate or deflate the price. Traders who base their decisions on these manipulated prices may suffer significant financial losses.
2. Arbitrage: Flash loans can be utilized to exploit price discrepancies between different decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Attackers can borrow funds from one exchange, take advantage of the price difference on another exchange, and execute arbitrage trades for profit. While this type of attack is not inherently malicious, it can still impact the profits of legitimate traders.
Learn How to Build a Flash Loan Arbitrage Bot here
3. Smart Contract Exploits: Flash loans can be leveraged to exploit vulnerabilities present in DeFi smart contracts. For example, attackers may take advantage of reentrancy bugs or integer overflow errors to siphon funds from the contract or perform other unauthorized actions. These attacks can lead to significant financial losses and undermine the trust in affected protocols.
It's important to note that flash loans themselves are not vulnerabilities. They are innovative financial tools that provide liquidity and flexibility to users. However, malicious actors exploit the unique characteristics of flash loans to orchestrate sophisticated attacks that can have far-reaching consequences.
Examples of Flash Loan Attacks
Here are two notable instances of flash loan attacks that occurred in the DeFi space:
Euler Finance
On March 13, 2023, Euler Finance, a DeFi lending protocol, fell victim to a flash loan attack. The attack unfolded as follows:
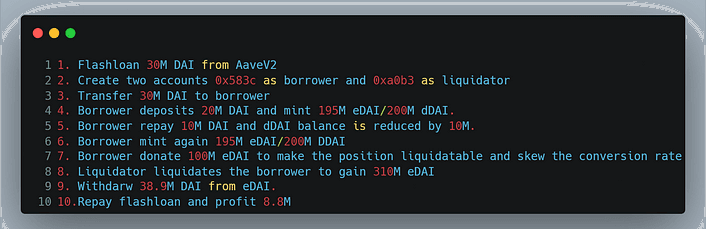
- The attacker initiated a flash loan from Aave, borrowing 30 million DAI.
- Two contracts were deployed: one for lending and another for liquidation.
- The attacker utilized the deposit function and pledged 20 million DAI to the Euler Protocol contract, receiving 19.5 million eDAI in return.
- Leveraging the mint function, the attacker borrowed 195.6 million eDAI and 200 million dDAI, surpassing their initial deposit.
- To repay their debt, the attacker used the remaining 10 million DAI borrowed from the flash loan, thereby destroying 10 million dDAI.
- The attacker further borrowed 195.6 million eDAI and 200 million dDAI by calling the mint function again.
- By donating 10 times the amount needed to repay their debt (sending 100 million eDAI) through the donateToReserves function, the attacker initiated the liquidation process.
- As a result, the attacker obtained 310 million dDAI and 250 million eDAI by calling the liquidate function.
- Finally, the attacker withdrew 38.9 million DAI, which was used to repay the 30 million DAI borrowed in the flash loan, resulting in a profit of 8.87 million DAI.
To learn more about this attack, you can read the full article here.
GDS Hack
On January 3, 2023, a flash loan attack targeted the GDS project on the Binance Smart Chain. The attack unfolded as follows:
- The exploiter initiated a flash loan, borrowing 2.38 million USDT.
- The exploiter exchanged 0.6 million USDT for 3.4 million GDS tokens.
- The remaining 1.7 million USDT, along with the obtained 3.4 million GDS tokens, were added to the liquidity pool.
- These assets were then exchanged for 2.2 million LP tokens on PancakeSwap.
- By collecting rewards from the GDS token contract, the attacker profited.
- The LP tokens were transferred to another contract, and this process was repeated approximately 70 times to maximize rewards.
- Once the desired rewards were collected and the liquidity was depleted, the flash loan amount was repaid.
As a result of this attack, the exploiter obtained 39,000 USDT and nearly 10.3 million GDS tokens, valued at approximately $148,000.
For more information on the GDS hack, you can read the full article here.
C.R.E.A.M. Attack, October 2021 - Loss of ~$130m
- The hacker borrowed $500m DAI and $2bn ETH with separate addresses.
- By utilizing a series of trades and using the loans as collateral for more loans, the attacker artificially doubled the price of yUSD and repaid the loans.
- The attacker borrowed all the liquidity from the C.R.E.A.M. Ethereum v1 markets using the remaining $1bn of collateralized crYUSD.
- The post-mortem by C.R.E.A.M. identified the vulnerability in the price calculation of the wrappable token as the key issue.
xToken Attack, August 2021 - Loss of ~$4.5m
- This attack involved the use of a flash loan to manipulate the price of the xSNX token and unauthorized calling of a function.
- The hacker exploited the artificial arbitrage created by the price manipulation of xSNX.
- As a result of this attack, xToken decided to retire the xSNX product due to its complexity.
Pancake Bunny Attack, May 2021 - Loss of ~$200m
- The hacker utilized PancakeSwap to borrow BNB and manipulate the price of USD/BNB and BUNNY/BNB.
- By manipulating the prices, the attacker acquired a significant amount of BUNNY tokens.
- The attacker then dumped the acquired BUNNY tokens and the remaining BNB, resulting in a loss estimated at around $200m at that time.
Platypus Finance ($8.5 Million)
- In February 2023, the Platypus Finance project on the Avalanche network suffered a flash loan attack, resulting in an $8.5 million loss.
- The attacker borrowed 44 million USDC from Aave and utilized it to stake and borrow more funds from the PlatypusTreasure contract.
- By exploiting a logic issue in the emergencyWithdraw function of the MasterPlatypusV4 contract, the attacker was able to directly withdraw the staked LP tokens without repaying the borrowed funds.
- The vulnerability stemmed from the function not properly checking the user's repayment status, enabling the attacker to bypass the repayment requirement.
Alpha Homora Protocol ($37 Million)
- Alpha Homora, a leveraged yield farming protocol, fell victim to the largest flash loan attack of 2021, resulting in a loss of $37 million.
- The attacker leveraged the Iron Bank lending platform from Cream to repeatedly borrow sUSD through Alpha Homora's dapp.
- With each borrowing cycle, the attacker doubled the borrowed amount and lent the funds back into Iron Bank, receiving cySUSD in return.
- By using flash loans to repay the borrowed sUSD and borrow more, the attacker accumulated large amounts of cyUSD and utilized it to borrow various other cryptocurrencies from Iron Bank, including WETH, USDC, USDT, and DAI.
Steps to Prevent Flash Loan Attacks
To mitigate the risks associated with flash loan attacks, the following preventive measures can be implemented:
Decentralized Pricing Oracles
Flash loan attacks often rely on price manipulation. By utilizing decentralized pricing oracles such as Chainlink or Band Protocol, protocols can obtain accurate and reliable pricing data for different cryptocurrencies. This reduces the vulnerability to attacks like the one that occurred with dYdX, where protocols relied on price feeds from a single decentralized exchange (DEX).
Time-Based Constraints
Introduce time-based constraints or restrictions on certain contract operations to prevent the rapid or simultaneous execution of multiple transactions within a short period. This can help mitigate the impact of flash loan attacks that rely on executing multiple transactions within a single block.
Limit External Dependencies
Reducing reliance on external contracts or dependencies whenever possible can help minimize the attack surface and potential vulnerabilities in the system. By limiting external dependencies, the overall security of the protocol can be improved.
Implement Access Controls
Employ access control mechanisms to restrict certain operations to authorized addresses or roles. This prevents unauthorized parties from interacting with critical contract functions, adding an additional layer of protection against potential attacks.
Limit Transaction Sizes
Restrict the maximum loan amount or borrowing limits for flash loans. By imposing limits, the potential impact of an attack can be mitigated, as the attacker's ability to manipulate large amounts of funds within a single transaction is significantly reduced.
Circuit Breakers
Implementing circuit breakers can be highly effective in preventing flash loan attacks. These automated mechanisms halt trading on a platform if specific conditions are met, such as a sudden drop in liquidity or a large price movement. Circuit breakers can prevent flash loan attacks by stopping large price movements, making it more difficult for attackers to manipulate asset prices.
High-Frequency Pricing Updates
Increasing the frequency of price updates within liquidity pools can help deter flash loan attacks. By querying oracles for fresh prices more frequently, the price of tokens within the pool gets updated faster, making price manipulation more challenging for attackers.
Time Weighted Average Pricing
Using Time Weighted Average Pricing can provide an additional layer of protection against flash loan attacks. Instead of relying on a single price calculation (mean or median), TWAP involves averaging prices across multiple blocks. Manipulating the TWAP requires manipulating the entire blockchain, making it more difficult for attackers to exploit flash loan vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
As the DeFi industry continues to evolve, it is crucial to address vulnerabilities and strengthen prevention mechanisms against flash loan attacks. While measures such as decentralized oracles, time-based constraints, limiting transaction sizes, circuit breakers, high-frequency pricing updates, and TWAP strategies can help mitigate risks, the industry as a whole needs to adopt more effective methods to combat flash loan exploits. With each incident, the ecosystem evolves and becomes more resilient to potential attacks, making DeFi a safer space for users and protocols alike.
Author: chandan